What Role Does Ecpr Play in Cardiac Arrest
Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation ECPR has been performed with increasing frequency worldwide to improve the low survival rate of conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation CCPR. Awareness and usage of ECPR are increasing all over the world.

Extracorporeal Pulmonary Resuscitation Ecpr Of Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
It is possible that more robust end-organ support is the key.

. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation commonly known as ECPR is a method of cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR that passes the patients blood through a machine in a process to oxygenate the blood supply. When patients present to the ED in the peri-arrest phases of cardiovascular collapse decisive action by the emergency physician can make the difference between life and death. Currently only about 10 percent of people survive a sudden cardiac arrest that happens in the field even fewer survive with normal neurological function.
Defining sudden cardiac arrest is difficult because it can be caused by any number of different. Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation ECPR ECMO during cardiac arrest Provides support to vital organs with perfusion gas exchange. In the case of IHCA further specifications are needed.
The number of in hospital cardiac arrest decreases Morbidity and mortality rates increase. These are the physician-based mobile medical teams that respond by helicopter HEMS or SUV usually arrive within 15 minutes and can be virtually. Sudden Cardiac Arrest Defined.
Today when a cardiac arrest victims heart stops if theyre not inside a hospital the chance of survival is less than 10 percent. Sudden cardiac arrest is one of the leading causes of death in the United States. ECMO or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is an advanced life support technique that provides cardiac and pulmonary support similar to cardiopulmonary bypass.
Additionally critical information necessary to determine whether a patient is a candidate for aggressive intervention is often unavailable or becomes. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation ECPR is a salvage procedure in which extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ECMO is initiated emergently on patients who have had cardiac arrest CA and on whom the conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation CCPR has failed. The first ambulance arriving does the ALS tasks and the 2nd ALS ambulance is there to support as a cardiac arrest is quite an intensive task.
Prague A Comparative Study Between a Pre-hospital and an In-hospital Circulatory Support Strategy ECMO in Refractory Cardiac Arrest NCT02527031. ECPR should only be used in highly selected patients with a cardiac origin of arrest. The use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during cardiac arrest extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation ECPR has increased in recent years 1 after evidence emerged that it was associated with better outcomes than conventional CPR for in-hospital cardiac arrest 2 3 4.
Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation ECPR is an advanced rescue therapy where an extracorporeal circuit is employed to support circulation in patients with cardiac arrest refractory to conventional CPR 1. Our new approach is called an ECPR Extra-Corporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation alert. What roles does ECPR fill in the management of cardiac arrest.
Moreover indications and contraindications may vary according to hospital experience level of the cardiac arrest team and readiness of ECLS deployment. A portable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ECMO device is used as an adjunct to standard CPR. ECPR extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation is the rapid deployment of VA-ECMO when conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation fails to provide return of spontaneous circulation.
To date there has been a lack of RCTs of ECPR and there are no prospectively validated criteria for ECPR indications or. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation ECPR is associated with improved survival for patients with shockable out-of-hospital cardiac arrest compared with standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR at all durations of professional CPR. Terms in this set 246.
In this blog post we discuss why Defibrillation and CPR need to be combined when attempting to save the victim of sudden cardiac arrest. Several studies have shown that among patients who experience in-hospital cardiac arrest better survival. What is new are the people in orange arriving latest.
After initial Basic Life Support BLS and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support ACLS by Emergency Medical Services EMS per existing EMS protocols patients with refractory cardiac arrest are transported to an ECPR capable emergency department with ongoing mechanical CPR and ACLS for possible initiation of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation for cardiac arrest. ECPR may be considered for select cardiac arrest patients for whom the suspected cause of the cardiac arrest is potentially reversible during a limited period of mechanical cardiorespiratory support.
This success led some clinicians to attempt ECPR in highly. Reported survival rates range from 15 to 17 for in-hospital cardiac arrest IHCA and from 8 to 10 for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA 1-3. The ECPR alert is designed to change those numbers.
ECPR RCTs are happening. A patient who is deemed to be in cardiac arrest. This protocol is for people who are in ventricular fibrillation or refractory ventricular tachycardia which are irregular heart rhythms that arent compatible.
Emergency Cardiopulmonary Bypass for Cardiac Arrest n40. Cardiac arrest may happen as an unexpected event in patients admitted to the hospital for other causes but could also be the natural evolution of an acute critical illness in which ECPR could be interpreted as a late intervention for a moribund patient possibly candidate to an earlier circulatory support system. More people are leaving the hospital to return to their loved ones their work and their lives.
A potential role for ECMO in the treatment of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA is especially appealing. Vienna Hyperinvasive Approach in Cardiac Arrest n170. Many but not all of the observational studies showed overall favorable neurological outcomes in those who receive ECPR compared to conventional CPR.
The evidence supporting ECPR comes from observational studies in the past two decades in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and studies looking at ECPR in in-hospital cardiac arrest. There is insufficient evidence to recommend the routine use of extracorporeal CPR ECPR for patients with cardiac arrest. The ED ECPR Algorithm.
Despite numerous studies and detailed guidelines survival after cardiopulmonary resuscitation for sudden cardiac arrest remains low. Provides vital organ support while treating reversible causes. ECPR offers a promising mechanism to mitigate multiorgan injury and allow time for the institution of supportive interventions required to effectively treat cardiac arrest.

Ecpr Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Ohca Download Scientific Diagram

Flowchart Of Study Patients Ecpr Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Download Scientific Diagram
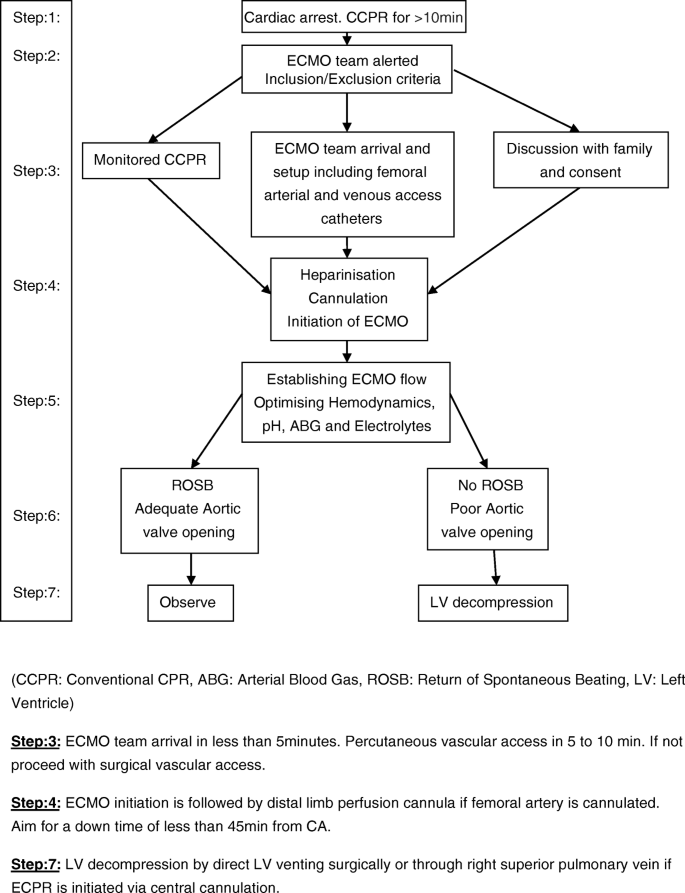
Ecpr Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Springerlink

Ecmo Ecpr Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
No comments for "What Role Does Ecpr Play in Cardiac Arrest"
Post a Comment